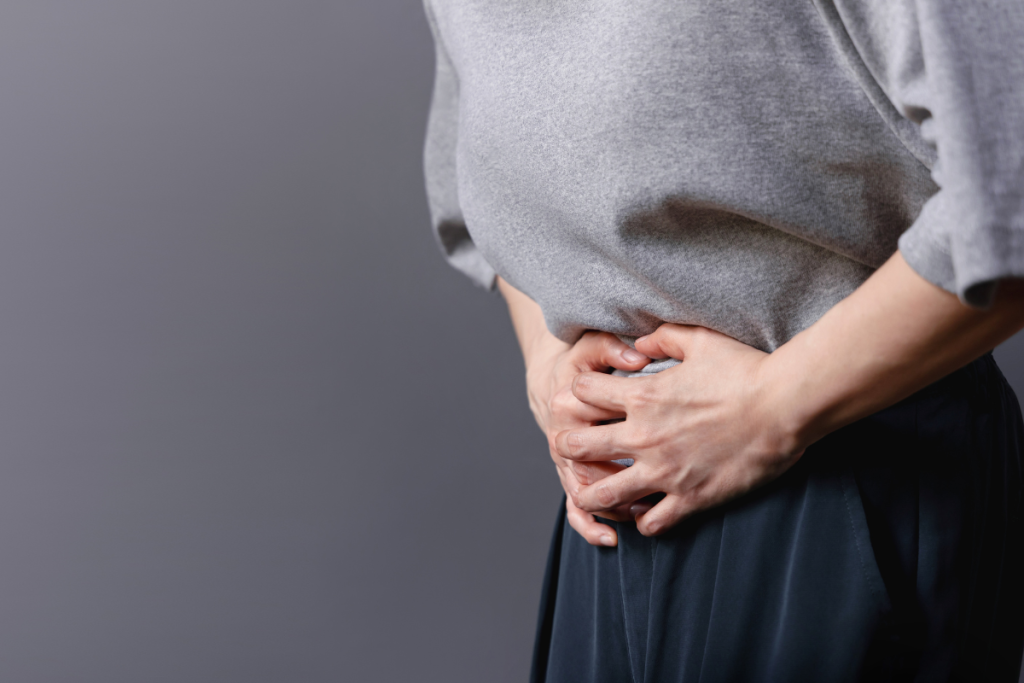
The early stages of ovarian cancer are challenging to diagnose. There is no accurate diagnostic test for early diagnosis, and symptoms are vague and easily confused with gastrointestinal problems such as constipation and bloating.
However, this does not mean that women are powerless. Knowing the symptoms and risks of ovarian cancer is the best defense against the disease.
Symptoms of ovarian cancer
Pelvic exams are important to women’s health, but unfortunately, most ovarian tumors are difficult to diagnose. Health care providers screen for cervical cancer, such as Pap and HPV (human papillomavirus), but do not diagnose cervical cancer. In most cases, a woman’s ultrasound or CT scan will show ovarian cancer. All this means that the disease is often late, when the cancer is advanced and can spread to other parts of the body.
Contact your doctor or gynecologist if you notice the symptoms of ovarian cancer more often than usual.
–Abdominal or pelvic pain
-Inflammatory bowel disease
-Malnutrition/malnutrition
-Feeling full after a small meal (premature satiety).
-Excessive or frequent drinking
You may also experience:
–fatigue
-Abdominal contractions
-Back pain
-Sex hurts
T-raffic jam
-Period changes, such as heavy or irregular bleeding
-Stomach bloating occurs during weight loss
Causes of ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is the fifth leading cause of cancer death in women, but the American Cancer Society reports that a woman’s lifetime risk is still very low. In the United States, less than 1% of women with no family history or other risk factors develop ovarian cancer.
Ovarian cancer is more common in postmenopausal women and increases with age. Half of all cases of ovarian cancer occur in women age 63 and older, and it affects white women more often than black women.
Other factors that may increase the risk include:
overweight or obese
Your first child in 35 years or never being pregnant
The use of hormonal preparations after menopause
Family history of ovarian, breast, endometrial, or colon cancer
BRCA1 and BRCA2, gene mutations associated with Lynch syndrome and other cancers
personal history of breast cancer
Smoking increases the risk of certain types of cancer. It could also be linked to a higher chance of:
Treatment of in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Hormone replacement therapy
Factors that reduce the risk of ovarian cancer
For women at risk of ovarian cancer:
Having a baby before the age of 26 (the risk decreases with each subsequent pregnancy).
breastfeeding
Take birth control pills.
Temporary use of the IUD (intrauterine device).
Pelvic surgery includes hysterectomy, which involves removing the uterus, tubal ligation, which ties the fallopian tubes, and ovarian excision.
Genetic testing
As mentioned above, ovarian cancer can be hereditary. Women with a family history of cancer or sexually transmitted diseases should ask about genetic counseling and testing.
Genetic testing is also important after a diagnosis of ovarian cancer. Your treatment will include tumor removal and possibly chemotherapy, depending on the size and location of the cancer in your body. You can help by asking yourself and others to get tested for family mutations such as BRCA1 (type 1 cancer) or BRCA2.
Be proactive
Trust your intuition, get an annual pelvic exam, and educate yourself on the signs and risk factors of ovarian cancer. You know your body. If there is an error.